Role of enzymes to improve efficiency of feed in poultry diet
Content
Definition of the term enzyme
What are the types of enzymes?
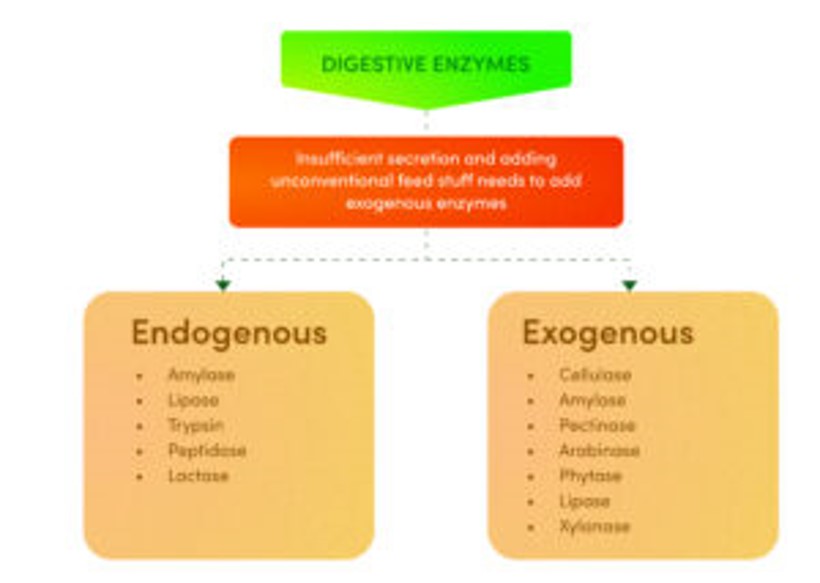
What enzymes should be added to the diet
How to calculate the values of enzymes used in the diet
The concept of enzyme in general
-
Enzymes are biological catalysts of a protein molecule. Accelerates chemical reactions. The molecules that enzymes exert influence on are called substrates, where the enzyme converts the substrate into molecules known as products. Most metabolic processes need enzymes in order to occur quickly enough to sustain life.
Enzymes in the poultry industry improve growth and provide protein, increasing the bird's consumption of food, as researchers have been working to extract the maximum possible representative energy from grains such as barley, wheat and oats.
It should also be known that these grains have a balance of energy and amino acids, as enzymes are better than maize used in poultry feed.
As enzymes in the poultry industry, which have been taught in order to improve growth results in birds, are water-soluble enzymes such as amylase and phytase, as phosphorus in the form of phytach, is the main compound of phosphorus stored in plants, and its percentage reaches 60-90% of total phosphorus, and there is polyscarase calsilase, glucanase and pantosanase.
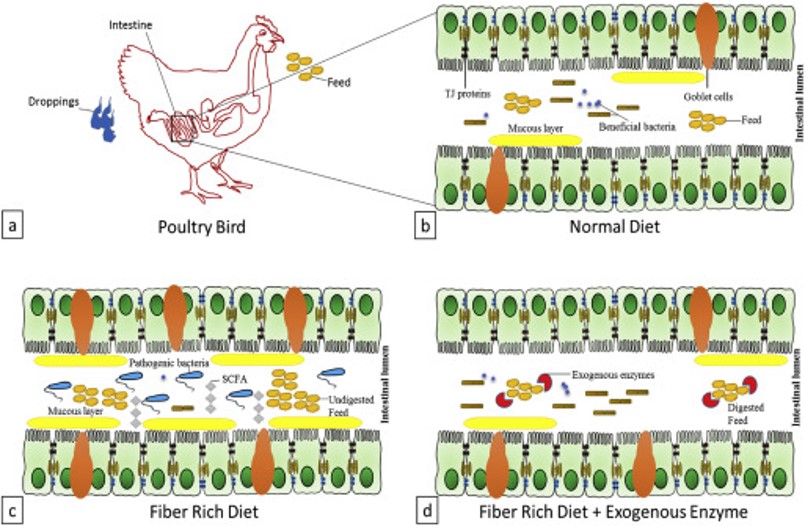
In the poultry industry, these enzymes release and break down the many undigested sugars within the digestive system, which are found in the packaging of grains of the grass family such as beta-glucnase, pentose sugar, cellulose and pectin.
Enzymes in the poultry industry improve growth and provide protein, increasing the bird's consumption of food, as researchers have been working to extract the maximum possible representative energy from grains such as barley, wheat and oats.
It should also be known that these grains have a balance of energy and amino acids, as enzymes are better than maize used in poultry feed.
As enzymes in the poultry industry, which have been taught in order to improve growth results in birds, are water-soluble enzymes such as amylase and phytase, as phosphorus in the form of phytach, is the main compound of phosphorus stored in plants, and its percentage reaches 60-90% of total phosphorus, and there is polyscarase calsilase, glucanase and pantosanase.
In the poultry industry, these enzymes release and break down the many undigested sugars within the digestive system, which are found in the packaging of grains of the grass family such as beta-glucnase, pentose sugar, cellulose and pectin.
Things to consider
The results obtained as a result of the addition of enzymes in the poultry industry show that they are very variable, but most of them can be considered acceptable, as these results are summarized in that enzymes improve growth. Although the bird's consumption of food increases, water consumption decreases, which reflects positively on the health status of the herd in general, and the state of the mattress in particular, which leads to a decrease in the mortality rate. This comes due to the decrease in diarrhea, as well as the decrease in the number of bacteria in the mattress, and the improvement of ventilation conditions, and it was noted that the final weight of the birds has improved, which results in a decrease in the production period time from two to three days, and for the same diet, as it was found that the consumption index has improved significantly by 14%.
Factors affecting the response to enzymatic additives
- The factors affecting the use of enzymes in the poultry industry are divided as follows:
Type of animal In ruminants there is no response to enzymes, because they exist naturally as a result of the microbial environment inside the rumen, which are enzymes that break down cellulose and non-starchy sugars, while we see that single-gastric animals are more responsive, especially birds.
Age The nutritional value of wheat and barley improves with the bird's age, but becomes less responsive after 8 weeks of age.
Sex There is no effect of sex on the response to enzymatic additives.
Inhibitors of proteolytic and digestive enzymes proteinase inhibitors and antiproteases:
Antigenic proteins:
Some proteins found in legume seeds have the ability to travel in their original form through the epithelial tissue of the intestinal mucosa to stimulate many immune reactions in addition to damaging the intestines. One of these substances is glycinin found in soybeans. These substances are characterized by their ability to resist the processes of denaturation by normal heat treatments or by the action of enzymes in the gut.
It is a group of proteins that interact with many proteolytic enzymes in the gut, such as trypsin inhibitors found in soybeans, which have a specific effect on its nutritional value. Non-thermally treated legumes, especially soybeans, contain two types of proteins, which are bound by trypsin and chymotrypsin enzymes secreted from the pancreas and intestines. The end result of the presence of such substances in diets is reduced digestion rates, increased internal loss of amino acids and consequently reduced animal production.
There are many substances that have harmful effects on the productivity of farm animals inside the feed or within the feed compounds themselves, these substances are divided into plant harmful substances, microbial toxins and substances resulting from feed manufacturing processes
First: Plant toxins
Many plant components have a harmful effect on the animal and these components may be found in the leaves or seeds inside the plants used in nutrition, and these substances can be divided into two main groups:
A - Group of materials affected by heat: They include lactins, proteolytic enzyme inhibitors and cyanogens, all of which are sensitive to the temperatures used during manufacturing processes.
B - Group of materials that are not affected by heat: It includes many soapy substances, gossypol, glucosinols, alkaloids, dragons and mimosin
The relationship of feed mixtures and enzymes in the poultry industry
There is a close relationship between feed mixtures in enzymes in the poultry industry, as most poultry diets are granulated in shape, allowing birds to increase their consumption and thus speed their growth. The granulation process has effects on feed mixtures, as it occurs as a result of high temperature due to the use of water vapor, as part of the many non-starchy sugars are destroyed, which makes the digestion rate of the diet high by birds. Second: It is a result of the heat used, some of the enzymes already inside the grains, break down and may disappear from 23 to 48%, except that many of the added enzymes break down and decrease their percentage, as a result of the granulation process, so I recommend either doubling the amount of enzymes added or adding them to drinking water if possible.
Types of enzymes in animal feeds
Xylinase enzyme
Phytase enzyme
Protease enzyme
Amylase enzyme
Pectinase enzyme
Libiase enzyme
Cellulase enzyme
Placebo-Cylylas
- Type of strain used
- Type of enzyme used
- The released value of the enzyme is based on the company producing the enzyme
- Using more than one enzyme in the same diet or not
- The use of other feed additives in the feed formula that have liberated values such as fatty emulsifiers, cryptocologists or the like.
- The method of mixing and manufacturing of feed
- The extent to which the enzyme is affected by heat The amount of oil used in the diet The style of the professor who installs the bush itself
The method of calculating the liberated values in animal gums
The difference between multiple enzymes and single enzymes
- Enzyme Manufacture
- Are the enzymes all from the same source or does each enzyme have a different source
- Do all enzymes have thermal stability, especially in piston manufactured feeds?
- What is better, single enzymes or multiple enzymes?

What is the best way to choose an enzyme
Bacterial or fungal Which is better and why?
What is the unit of the enzyme and do all enzymes have the same unit
Factors affecting the efficiency of enzymes in general before and after manufacturing
How to evaluate each enzyme separately theoretically and practically
Harmful substances in feed and their components
- Type of enzyme used
- Enzyme storage method
- Temperature used in manufacturing
- The degree of humidity used in manufacturing
- Type of feed produced
- How to store feed
- How to add feed additives to feed ingredients
- The method of manufacturing the feed itself
How to evaluate each enzyme separately theoretically and practically
Stabilizers sent by the enzyme manufacturer
Enzyme analysis methods in the laboratory
Thermal stability of the enzyme
The released value of each enzyme sent by the enzyme manufacturer